In this article
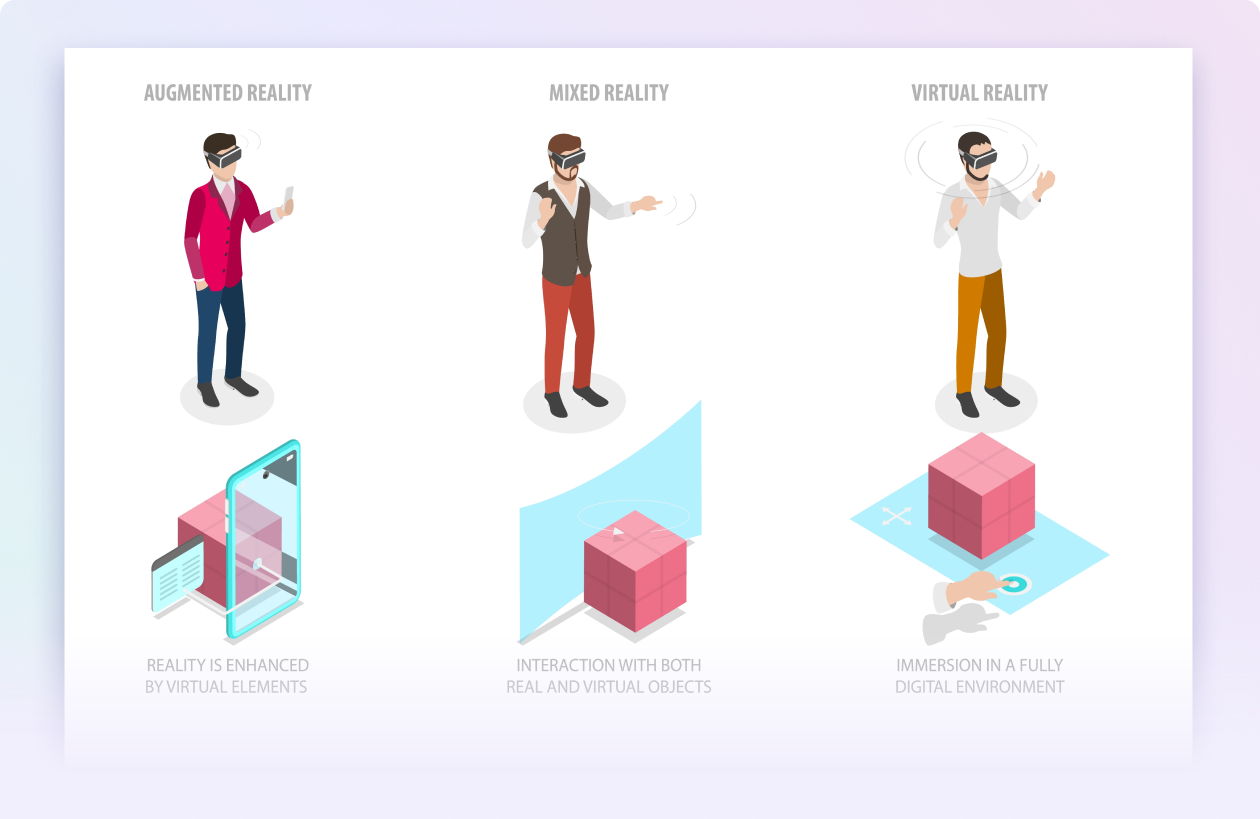
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?
Key features
Enterprise applications
The world of immersive technologies is rapidly expanding, with terms like Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) becoming more prevalent. Understanding the differences between these technologies is essential for enterprise leaders considering implementing these tools to enhance business operations and training programs. This article will define each technology, explore their unique features, and discuss their applications across various industries, with a focus on enterprise use cases.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a fully virtual environment, completely separate from the real world. Users typically wear a VR headset that tracks their movements and provides a 360-degree view of the virtual space.
Key features:
- Full immersion in a virtual environment
- Interactive 3D graphics
- Head and motion tracking
Enterprise applications:
- Training and education: VR is used for training simulations in industries like healthcare and manufacturing, providing a safe environment to practice skills. In the oil and gas industry, VR is used to train employees on operating complex machinery and handling emergency situations, allowing them to experience various scenarios without the risks associated with real-world training.
- Product development: VR is utilized to design and test new products, allowing engineers to collaborate in a virtual space and make real-time modifications.
- Remote collaboration: companies use VR to create virtual meeting spaces, facilitating remote teamwork and collaboration.
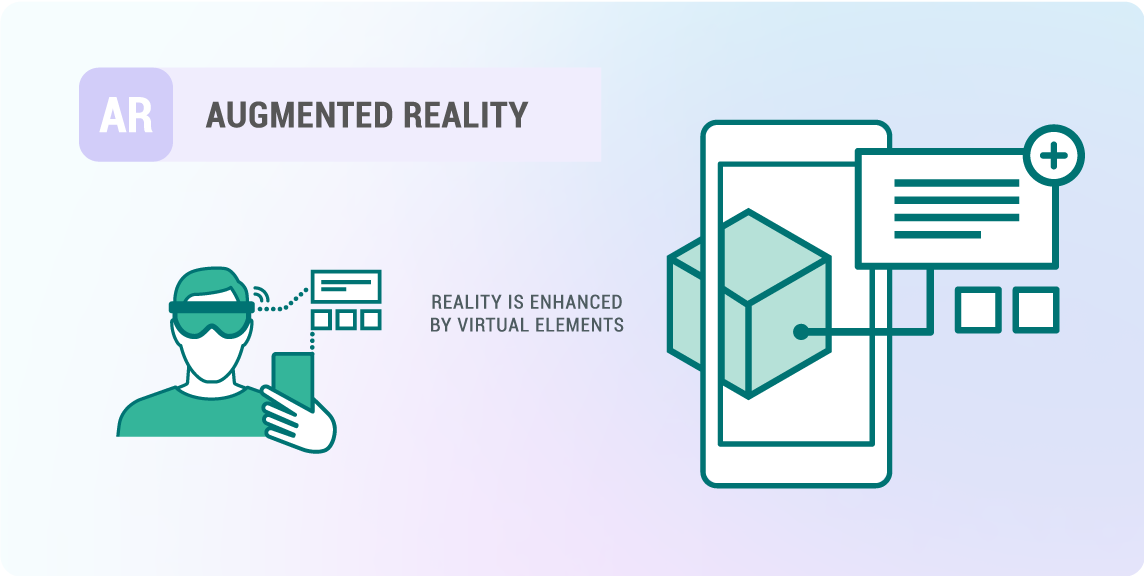
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their environment. This is typically experienced through smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses.
Key features:
- Real-time interaction between digital and physical worlds
- Overlay of digital information on physical objects
- Use of devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses
Enterprise applications:
- Retail and marketing: AR is used to allow customers to visualize products in their own environments, enhancing the shopping experience and reducing return rates.
- Field service: AR glasses can overlay maintenance instructions and diagnostics data onto equipment, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- Training and onboarding: AR is used to train employees on new processes and equipment, providing an interactive and engaging learning experience.
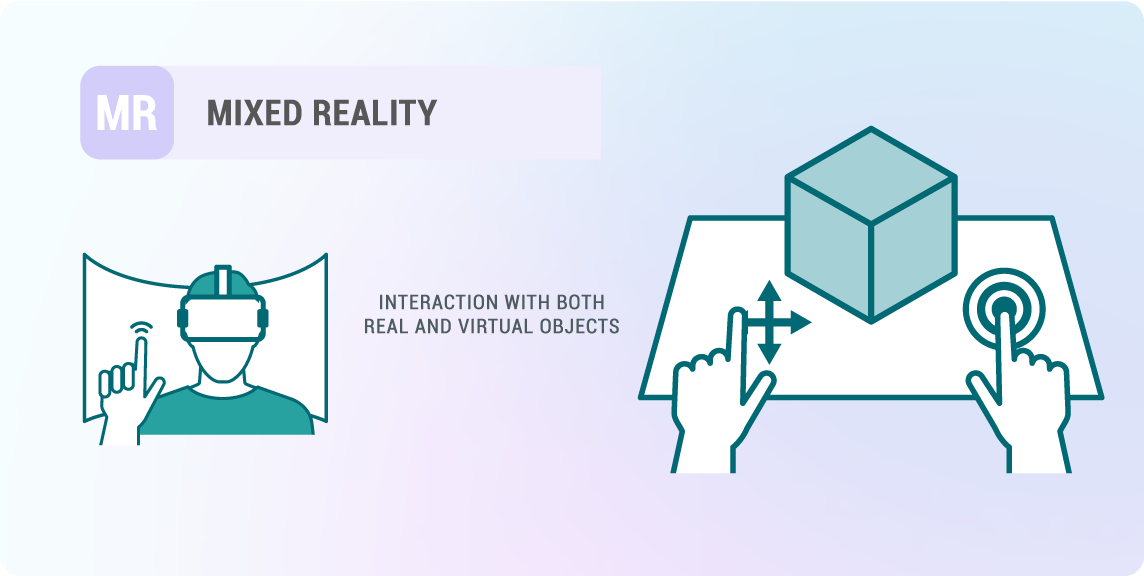
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?
Mixed Reality (MR) blends elements of both VR and AR, allowing real and virtual elements to interact in real-time. MR experiences are delivered through headsets that can map the physical environment and overlay digital content in a more integrated way.
Key features:
- Combination of VR and AR elements
- Interaction between physical and digital objects
- Use of advanced MR headsets like Microsoft HoloLens
Enterprise applications:
- Industrial design: MR is used to create digital twins of products, allowing engineers to interact with and test designs in a real-world context without physical prototypes.
- Healthcare: MR is used in surgical planning and medical training, providing a blend of real patient data and virtual simulation. Surgeons can practice complex procedures with MR before performing them on actual patients.
- Remote assistance: MR is used to provide remote assistance to technicians, overlaying step-by-step instructions and schematics onto equipment, reducing downtime and improving accuracy.

Key takeaways
VR, AR, and MR are transforming how enterprises interact with digital and physical worlds. Each technology offers unique capabilities and applications, making them valuable tools across various industries. By understanding their differences, enterprise leaders can better appreciate the potential of these immersive technologies and how they might be used to enhance business operations, training, and collaboration.
Contact us for more insights on how immersive learning can elevate your business training programs.